Glossary
Water Quality

Activated Carbon
A water filter component containing carbonaceous material that traps contaminants during the water filtration process. The material is derived from charcoal and produced by pyrolysis of organic materials of materials, which may include coal, coconut shells, wood, sugarcane bagasse, soybean hulls and nutshell.
Adsorption
The process by which a thin layer of molecules adhere to the surfaces of liquids or solid bodies. In classic water filtration, chlorine will adhere to activated carbon.

Aerators
A device located at the tip of a faucet that controls the amount of water that flows out and maintains the same perceptible flow rate.

Brine solution
Salt added to a water softening system’s brine tank that will ultimately replace the calcium and magnesium during a process called ion exchange.

Bypass valve
A valve installed on the pipe leading to a whole-home water softener or filtration system, designed to allow the homeowner to bypass the filtration or softening system to use city water for gardening or other purposes.

CaCO3, or Calcium carbonate
A chemical compound substance derived from calcite, aragonite, and limestone minerals in rocks that can enter your water supply and build up in your plumbing system, fixtures, and appliances.
Chloramine
A secondary disinfectant formed when ammonia is added to chlorine to treat drinking water.

Chlorine
A chemical disinfectant added to the public water supply to kill bacteria, viruses, and protozoans, commonly found in water supply reservoirs, water mains, storage tanks

Corrosive Agents
Chemicals that can destroy and corrode metal. For example, Chlorine is a corrosive acid and oxidizer that can destroy parts of your plumbing system over time.

Disc
A device that operates in pairs to allow full flow, partial flow or shut off of a faucet with less wear on the entire plumbing system.

Flapper (also known as the flush valve seal)
The plug in a toilet that falls against the drain hole (flush valve drain seat) on the bottom of the tank and holds water in until the next time you flush.

Flush ball (also known as tank ball)
A ball within your toilet tank, typically found in older toilets for the purpose of controlling the water moving from the tank to the bowl.

Gasket
A mechanical seal that fills the space between two or more connecting surfaces within your plumbing system to prevent water leaks while under compression.
Geosomin
A naturally occurring compound found in soil that has a strong, earthy taste and odour, even when found in our drinking water.

GPD (Gallons per day)
The measurement used to express the actual flow rate of a point-of-use water filtration system.

Granulated Carbon Block
A powdered block carbon material that most carbon water filters are made with.

Herbicides
A substance that is toxic to plants and is used to destroy unwanted vegetation.

Human Carcinogens
Substances and exposures that can lead to cancer in humans.

Inorganic Compounds
Any compound that is not an organic compound such as carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbonates, cyanides, cyanates, carbides, and thiocyanates.

Insoluble Soap Deposits
Compounds formed when sodium ion in soap is replaced with calcium and magnesium in water, making the soap harder to dissolve
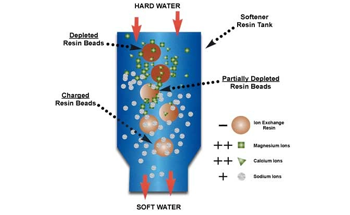
Ion Exchange
Process in which ions of one substance are replaced by similarly charged ions of another substance. In the case of water softening, positively-charged sodium takes the place of positively charged calcium and magnesium on negatively-charged resin beads.

Limescale
A filmy, whitish deposit on pipes, dishes, and appliances caused by calcium, limestone, and other minerals found in our water supply.

Media Filter
A filter that uses different media like a anthracite coal, sand, and other materials for acid neutralization and removal of contaminants such as chlorine, sediment, iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide from drinking water.

Mineral Tank
The heart of a water softener is a mineral tank where the calcium and magnesium ions in hard water move onto small polystyrene beads, replacing the sodium ions from the brine solution.

Naturally Occurring Materials
Any product or physical matter, including minerals and metals, that comes from plants, animals, or the ground.

NTU (Nephelometric Turbidity Units)
The measurement used to determine water cloudiness, more specifically the intensity of light scattered at 90 degrees as a beam of light passes through a water sample.

Organic Compounds
Any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds in which one or more atoms of carbon are covalently linked to atoms of other elements, most commonly hydrogen, oxygen, or nitrogen.
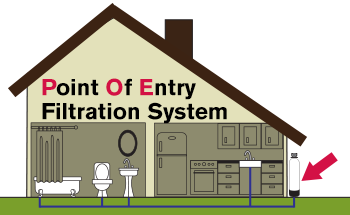
Point of Entry Filtration System (POE)
A large water filtration unit installed where the water enters your house to deliver filtered water throughout the home.
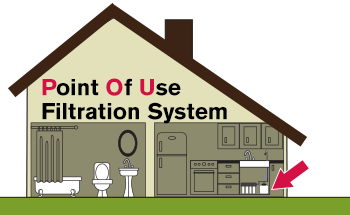
Point of Use (POU) Filtration System
A small water filtration unit placed under the sink or on a counter that provides filtered water at the point where the water will be used.

Polystyrene Beads (also known as resin or zeolite)
Negatively-charged beads that are placed in the water softener mineral tank to allow the ion exchange between positively-charged minerals and positively-charged sodium.

Pressurized Storage Tank
A special tank used for well water to create water pressure using compressed air.

Resin Tank Injector
The injector located in the interior of the resin tank used to regulate the flow of of saltwater from the brine tank to the water treatment medium that removes minerals from your water.

Reverse Osmosis Membrane
The main component in a reverse osmosis system that removes ions, molecules and larger particles from drinking water.

Shut-Off Valve
Valve positioned at points in your plumbing line to turn on, shut off, or control the flow of water to a plumbing fixture such as a faucet, tub, toilet or other plumbing fixture.

Soap Curd
A solid substance formed when soap interacts with calcium and other minerals found in hard water; also known as soap scum and insoluble soap deposits.

Storm Water Runoff
Rainfall that flows over various surfaces, including streets, asphalt, parking lots, rooftops and other paved surfaces.

Sub-Micron Post Filter
An optional filter used in the final microfiltration phase to reduce organic and sediment particles that may be not be captured by more traditional water filtration components.

Total Dissolved Solids (TDS)
Small amounts of organic matter and inorganic salts such as calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium, bicarbonates, chlorides, sulfates, that are dissolved in water.

Turbidity
Cloudiness or haziness of water used to determine water quality.
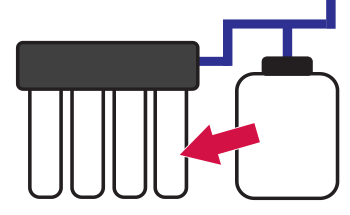
Water Filtration Canisters
Containers holding the filter used in Point-of-Use filtration systems.

Water Loop
A pipe loop in a regenerating water softener system designed to keep water flowing through the water softener and regenerate settled water with new and refreshed soft water.

Whole-House Water Filtration
A type of water treatment system that filters out contaminants from your entire home’s water supply.

Whole-House Water Softener
A type of water treatment system that eliminates hard water from your entire home’s water supply.
