Glossary
Attic Insulation

Active Ventilation System
A ventilation system that relies on a mechanical- and sometimes electrical- component like a fan to move air in and out of a building.

Attic Baffle (also known as Channel Vents, Vent Chutes, Proper Vents, and Rafter Vents)
Attic Baffles provide a channel for air to flow between your home’s soffits and attic space. They are typically made of polyvinyl chloride, rigid foam board, or cardboard.

Attic Cavity
The space between studs or joists typically filled with insulation.
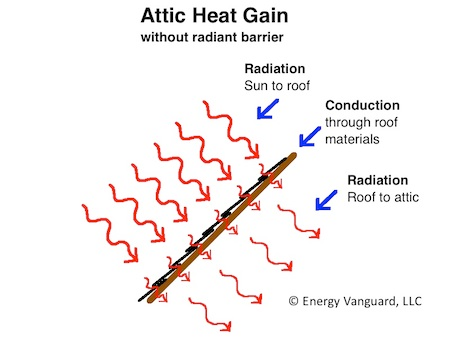
Conduction
The transfer of heat through direct contact with another substance.
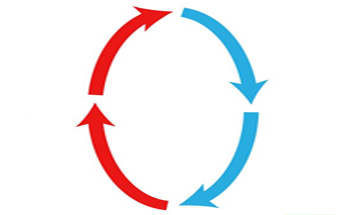
Convection
The transfer of heat through circulation in the air; hot air rises and cold air sinks.

Cooling Coil
(Technically referred to as a cool heat exchange coil) Controls the temperature of your home’s air in conjunction with your AC unit’s fan. A refrigerant cools the coil so that air that passes through it also becomes cool.
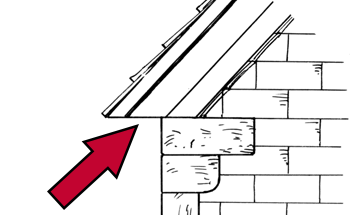
Eaves
The part of the roof that meets or overhangs the walls of your house.
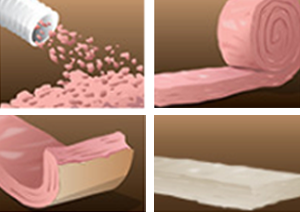
Fiberglass
A strong, lightweight fiber-reinforced plastic that slows the spread of heat, cold, and sound throughout homes.

Floor/Ceiling Joists
Parallel lengths of wood that run along the floor of your attic.

Gable Vents
Vents located on the wall that encloses the end of a pitched roof.

John Moore’s Whole-Home Philosophy
A holistic approach to home services that recognizes that all areas of the home can affect one another.

Knee Walls
A short wall (typically under 3 feet) that supports your attic’s rafters. Knee walls are common in older homes and section off the “useable” area of the attic.
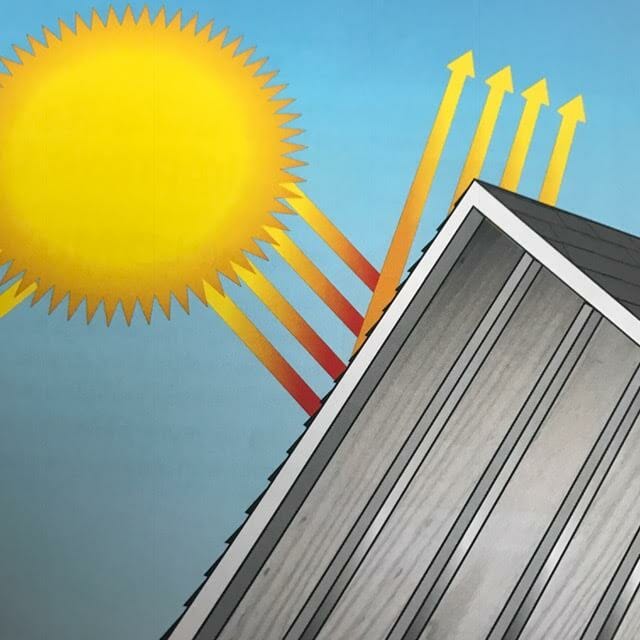

Low-Emissivity
A surface condition that emits low levels of radiant thermal (heat) energy, typical of shiny or reflective surfaces.
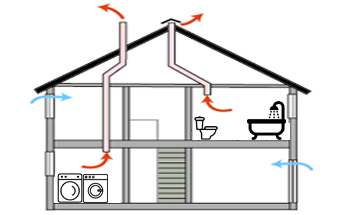
Passive Ventilation System
A ventilation system that relies on convection to move air in and out of a building.

R-Value
Measures the capacity of an insulation material to resist heat flow through conduction. The higher the R-value, the higher the capacity of a substance to resist heat flow.
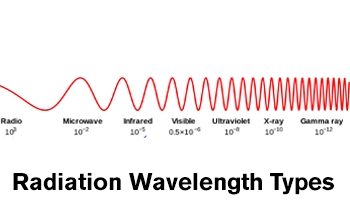
Radiation
The emission of heat through electromagnetic waves or as moving particles. For example, heat from the sun, a fire, or a hot surface is emitted through radiation.


Relative Humidity (RH)
The percentage of water vapor in the air relative to the amount needed for complete saturation at the same temperature. The higher the RH percentage, the more humid the air.

Ridge
The part of a roof where two sloped areas meet; the peak of a roof.

Ridge Vents
An air vent that runs along the ridge of a roof, which allows hot, moist air to escape from the attic further reducing cooling costs.
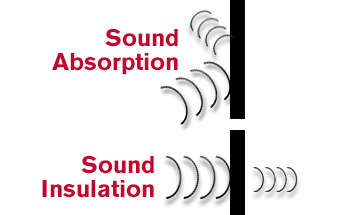
Sound Insulation and Absorption
The process of taking in sound waves to lessen how the amount of sound that travels through and is reflected off a given surface. Insulation absorbs sound, making it difficult for noises to travel through and bounce off of floors and walls in your home.


Scuttle Hole
The entry and exit door to an attic

Ventilation
The movement of air. In architecture, this applies to mechanisms and devices that allow for the intentional movement of air from the inside to the outside of your home and vice versa. Proper ventilation improves air-flow and air quality in a home, which can also reduce the cost of heating and cooling your home.

